Workload tool redesign Enhancing UX for effortless task allocation and workload balancing for agile teams
Context
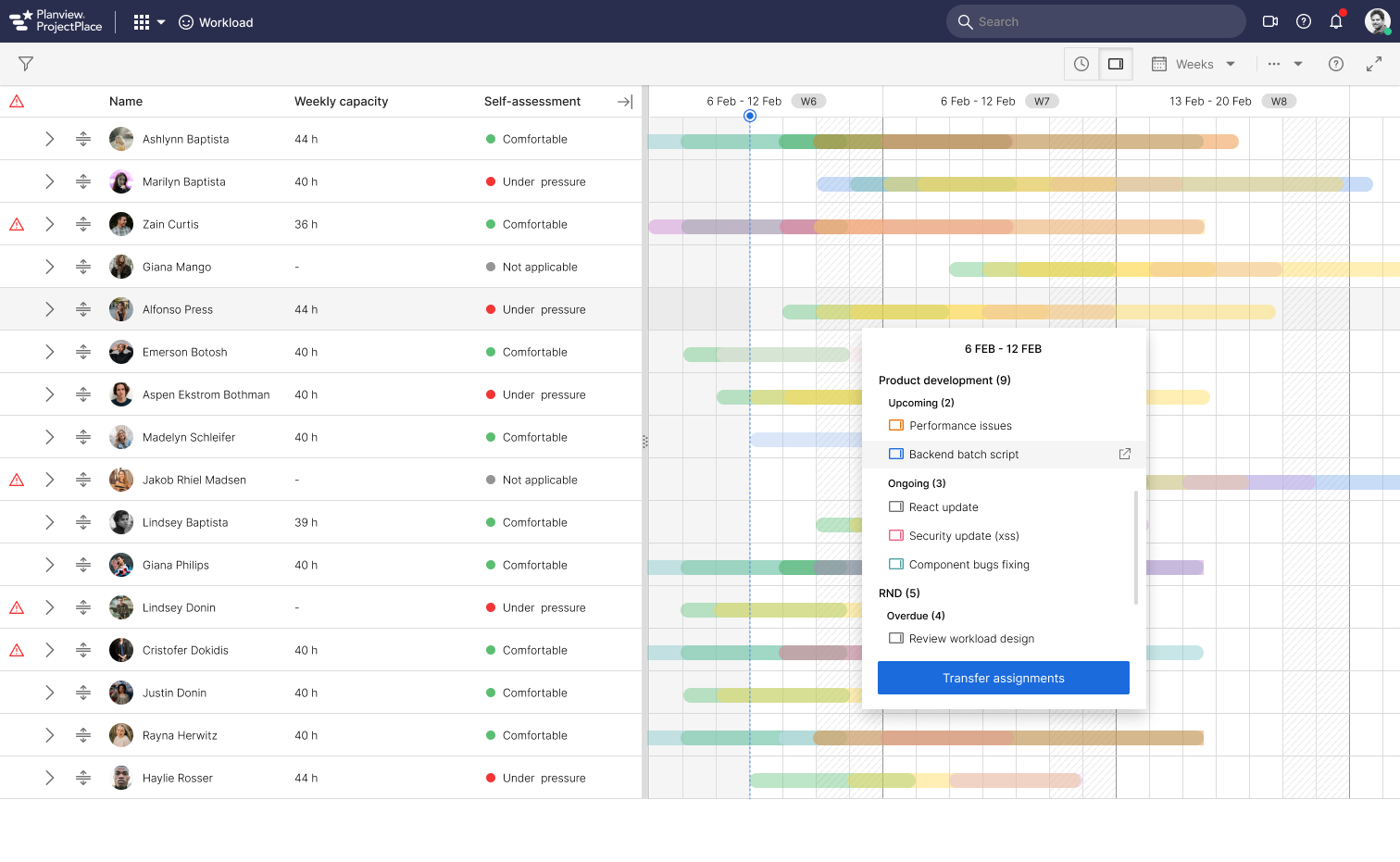
The Workload tool in Planview (Projectplace) shows how much work each team member has in all account workspaces. It helps workspace managers to see if someone has too much work and feels overwhelmed or if they don't have enough work and are underutilized.
The problem
The primary purpose of a workload tool is to determine if team members have too little or too much work assigned to them, allowing managers to take appropriate action. This typically involves redistributing tasks either within the same team or to another team. Currently, the tool lacks the capability to accurately gauge the capacity of individual team members within a workspace.
As a result, managers must rely on guesswork or direct communication with team members to make workload adjustments, leading to inaccuracies in task transfers and frustration for both managers and team members.
Additionally, recent enhancements to card attributes, such as the ability for users to specify planned start dates for tasks, have not been integrated into workload calculations, resulting in inaccuracies.
The workload tool was deemed essential for the sales process, yet its usage was unexpectedly low. This prompted the team to investigate the reasons behind the decreased usage compared to previous periods, highlighting the urgency of identifying the root cause.
My role & responsibilities
In a team comprising of six members, including one designer, one automation engineer, two backend developers, and two frontend developers, I served as both the interaction and visual designer, as well as the scrum master.
Took part in the primary user research, created wireframes, invision proptotypes and design iterations.
Collaborating closely with the Design System Team, I contributed to the formulation and documentation of design guidelines for enhancing the new workload tool.
My responsibilities also include ensuring alignment between the Design System Team and Product team throughout the enhancement process.
Following approximately 10 sprints spanning 4.5 months, we successfully launched the MVP to our customers.
Objectives
To address this issue
- capturing the capacity of each workspace member weekly is imperative.
- The workload views should take the planned start date for cards into consideration while visualizing capacity and assignments.
- Uplift user experience (with new Design System Components and patterns).
It's vital to align capacity with reported time on cards weekly, providing managers with accurate insights into individual workload distribution. This facilitates optimal assignment transfers and ensures balanced workloads across the team/workspace.
Challenges
- Relatively old code, Frontend bugs and performance issues when handling high volumes of data from all the accounts.
- Multiple users can report on same card (task or assignment). It was not very clear to us, to how to represent available time for each user once they report time.
- Tool is relatively new to us as it was previously developed by another team in the company. So there was bit of learning curve required for all of the team members.
Old design and our findings
I have conducted an initial design sprint with developers, Product owners and other designers from our design community to discover and decode the core problem for the tool.
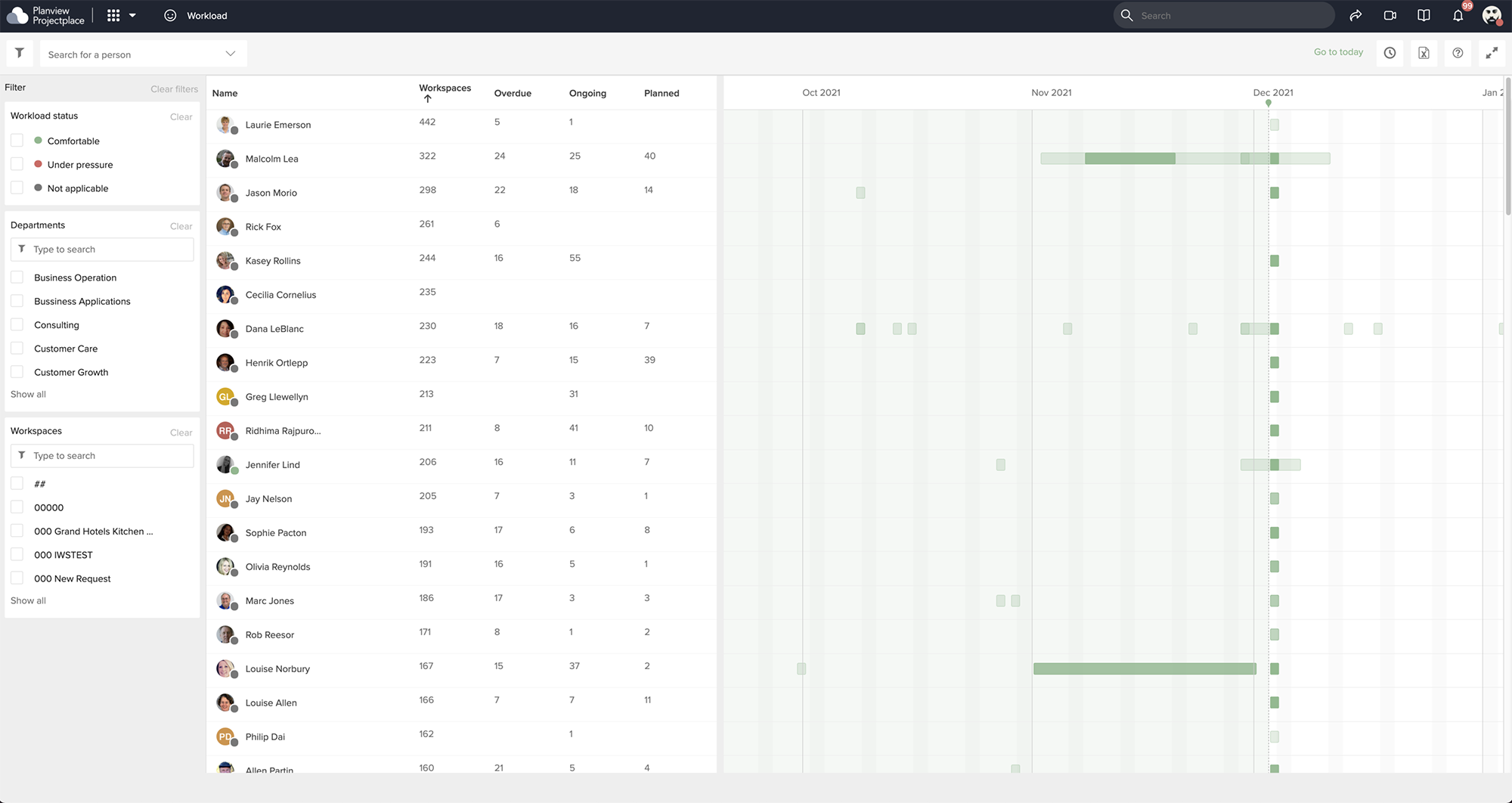
After our research we found some issues and decided to take some actions as shown below.
| Issue | Possible solution |
|---|---|
| The tool lacks the capability to account for the weekly work hours of each member, thereby casting doubt on the accuracy of individual workload assessments. | Introduce entering of capacity (in hours/week) field for each member in their settings page. Also make it editable by Admins in the workload tool. |
| Only heat map view is available. Customers can’t completely relay on this view. They wanted to see the number of tasks as well as the time spent on their assigned tasks against their capacity per week. | Introduce capacity view and clearly communicate each member’s work vs capacity numbers, so that admins can easily manage their workload. |
| Lot of bugs in the Frontend code making its usage very less. Old tool has very less automation test coverage. | Developers decided to introduce new design system components to enhance the tool and improve its performance . Also take care of the bugs. Introduce automation tests to reduce the bugs. |
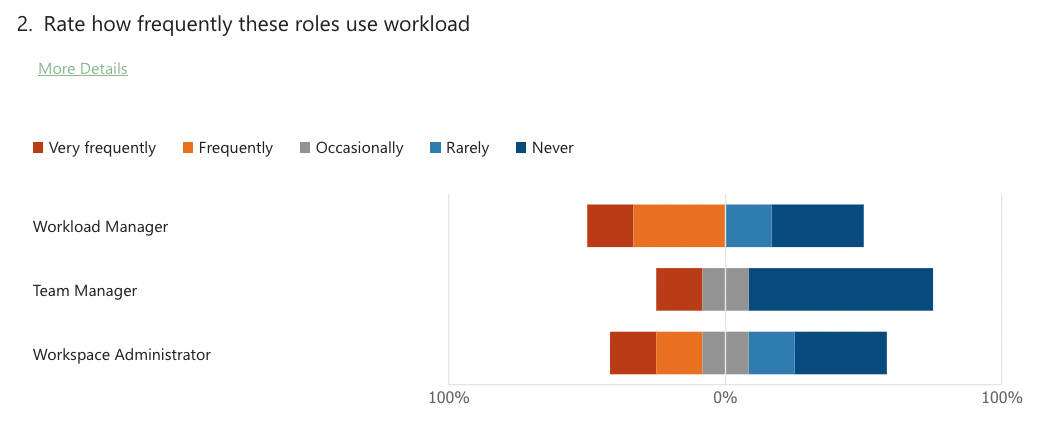
Initial survey and prototype testing
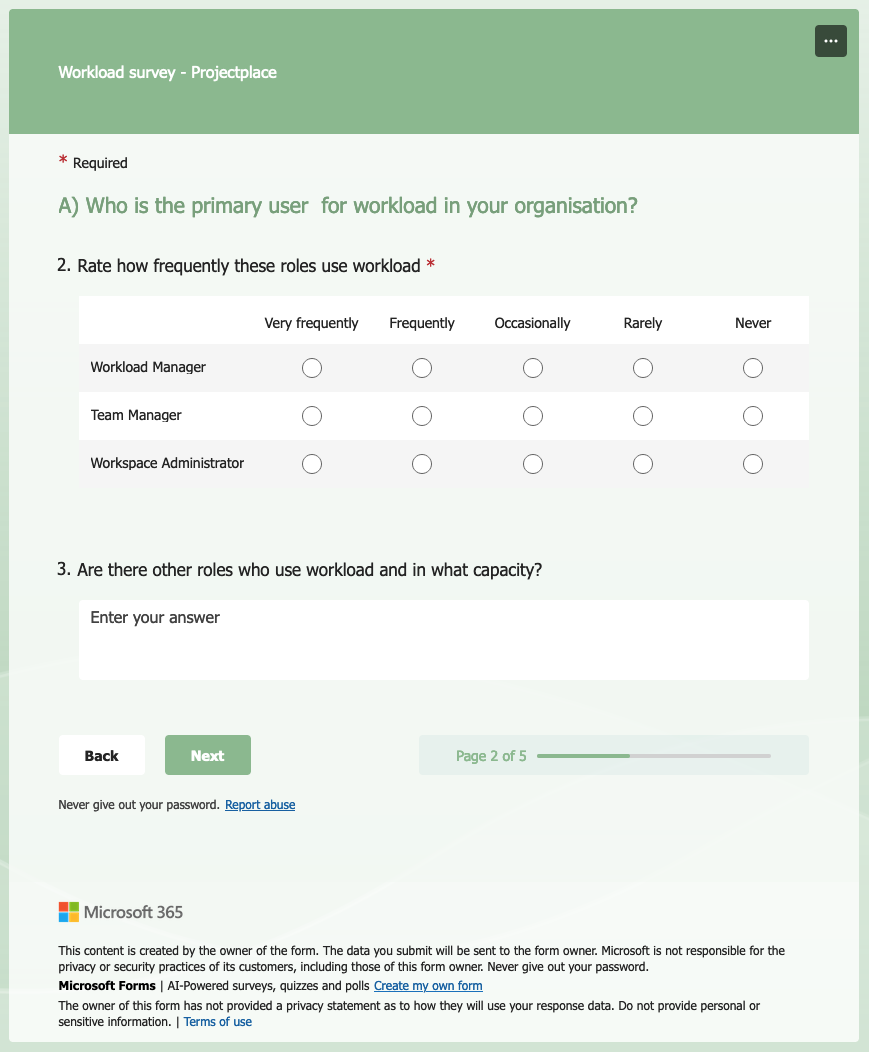
After our findings and possible solutions we had in our mind wanted to make sure that these solutions solve user’s problems. We sent them about 10 questions and analysed the results.
We have considered following personas/roles to gather feedback/testing
- Account admins
- Team admins
- Workspace admins
- Team members
Survey questions
Invision prototype
We have conducted a remote testing (3 groups separately consisting 5 users in each group) and a small survey. We have given them 3 tasks and noted our findings.

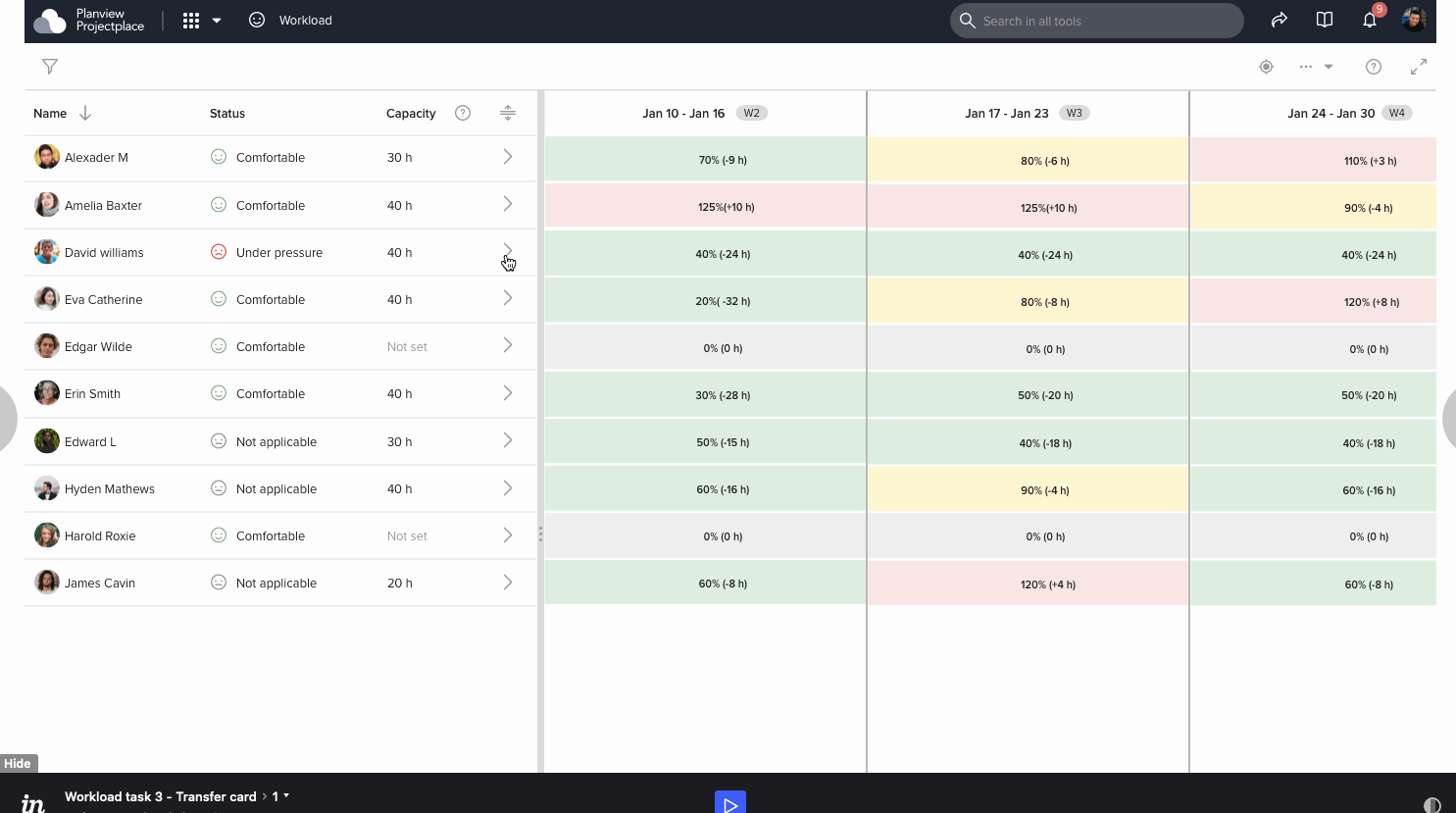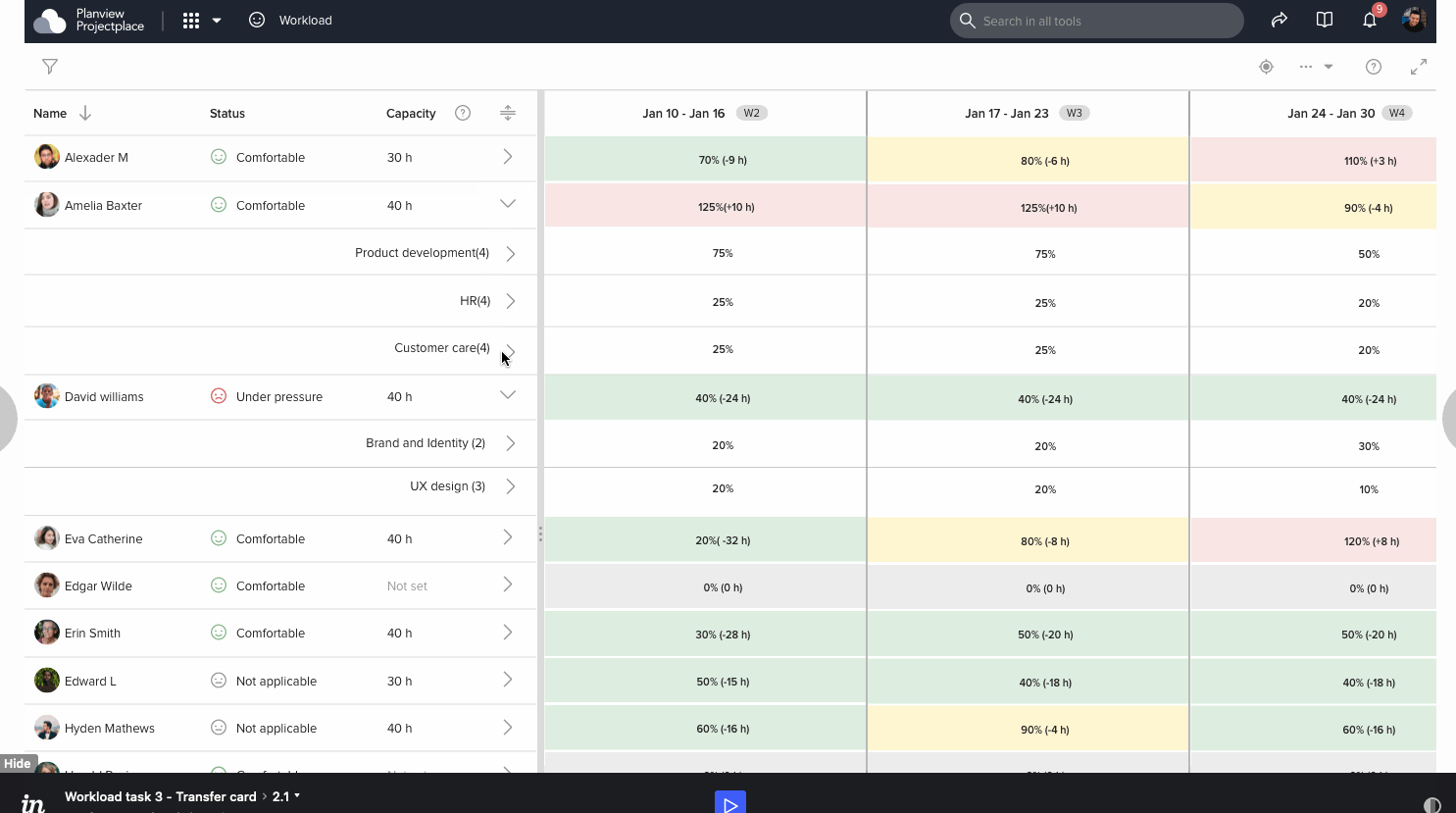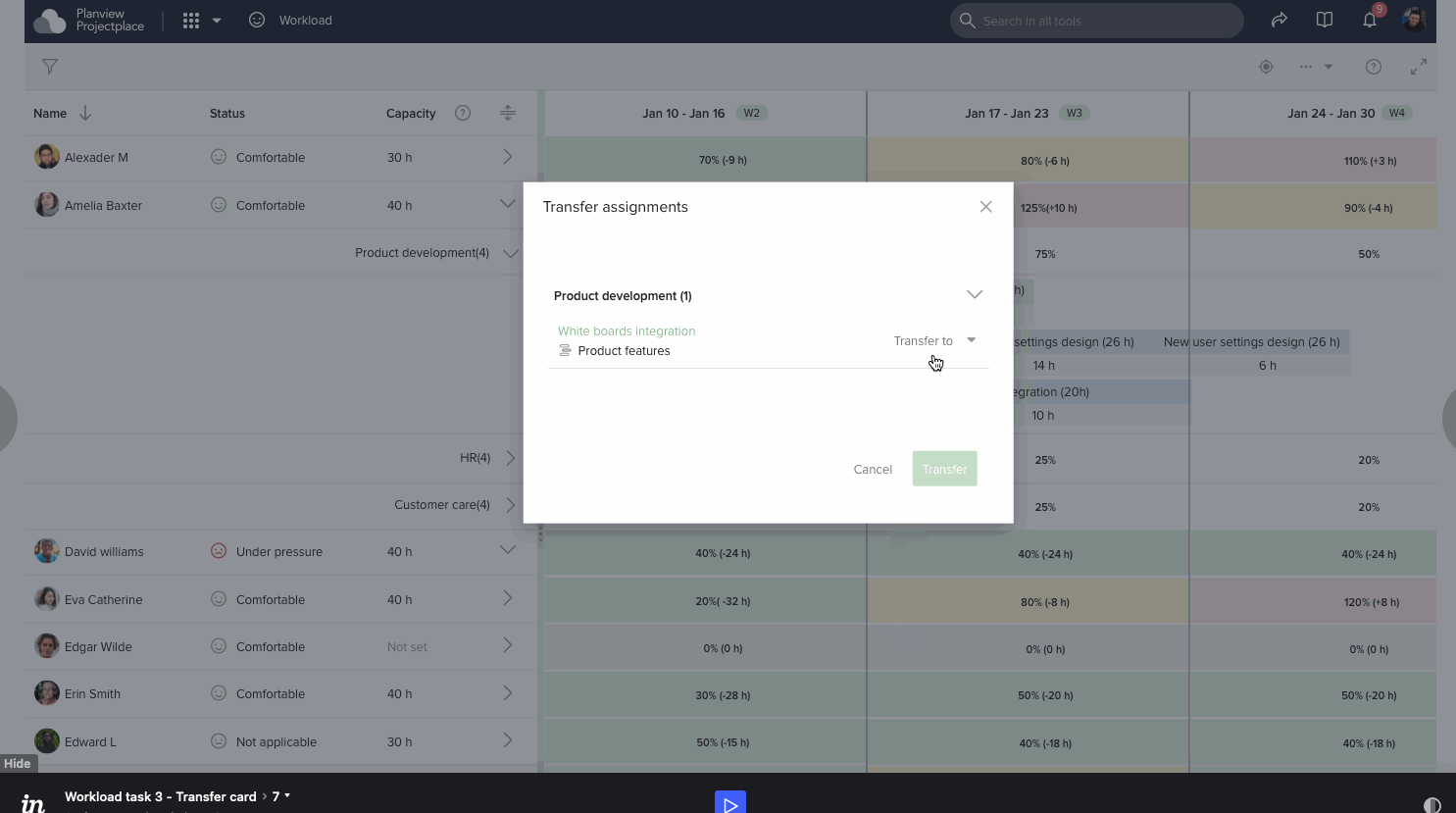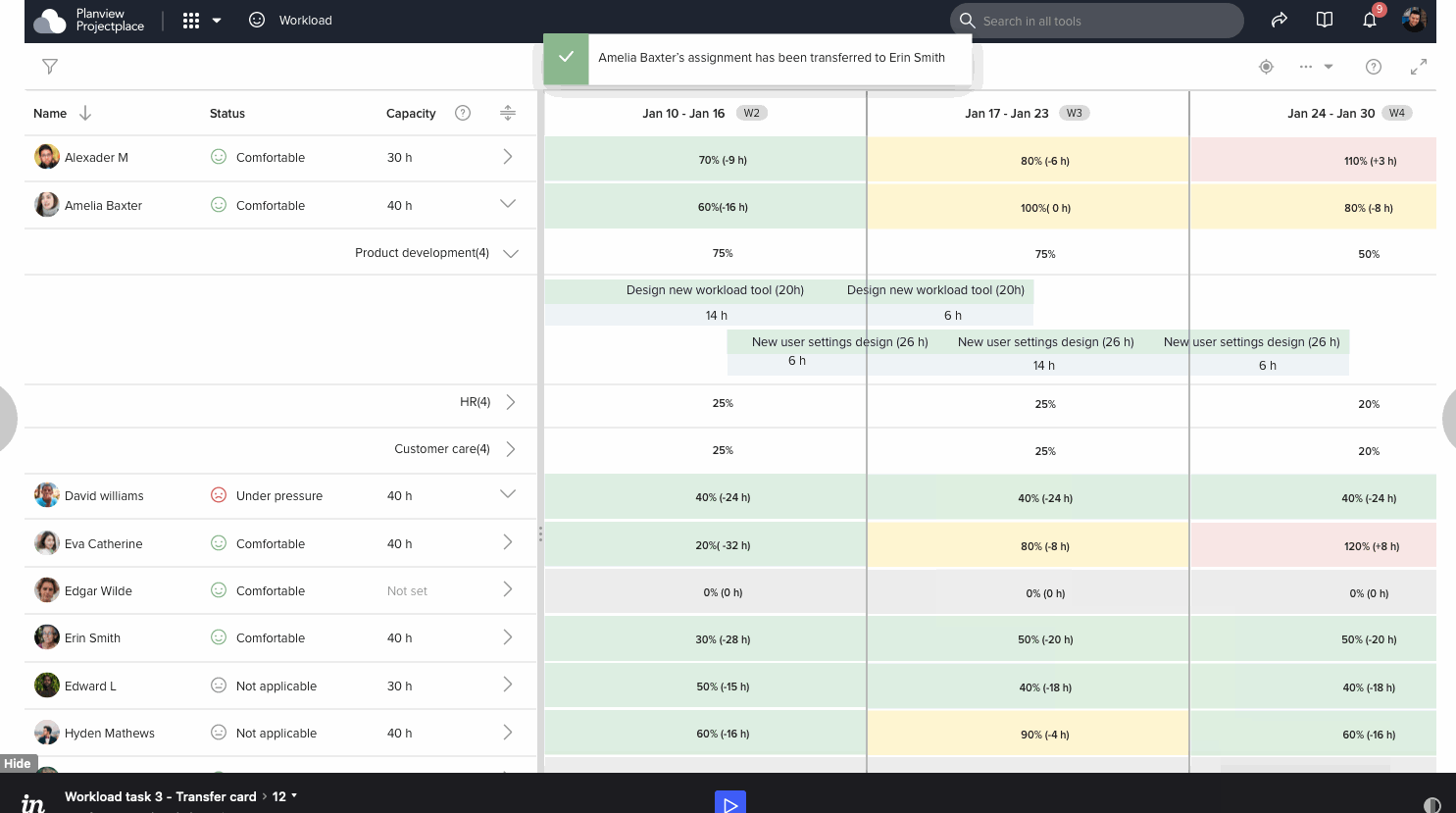
Prototype and survey analysis

Brainstorming
Based on our research findings from Surveys, Invision prototype testings, I have started working on further details, improving the designs basd on feedback from team and other stakeholders.
Dvelopers handoff & Final result
Documentation screens
I have handed over the design documentation and specifications once, we agreed upon the final designs in Zeroheight tool.
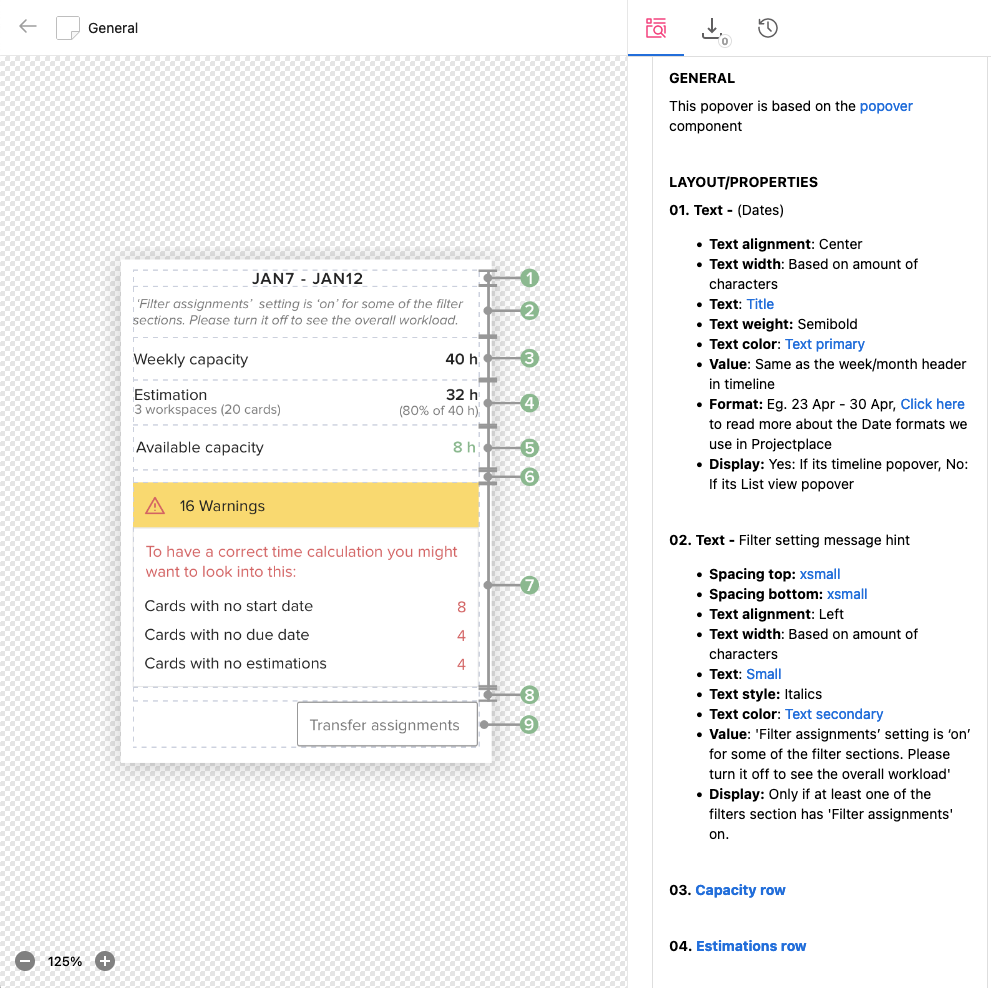
Final screens
After few iterations and a number of grooming meetings we have decided a design and started developing. Below is the gist of implemented design
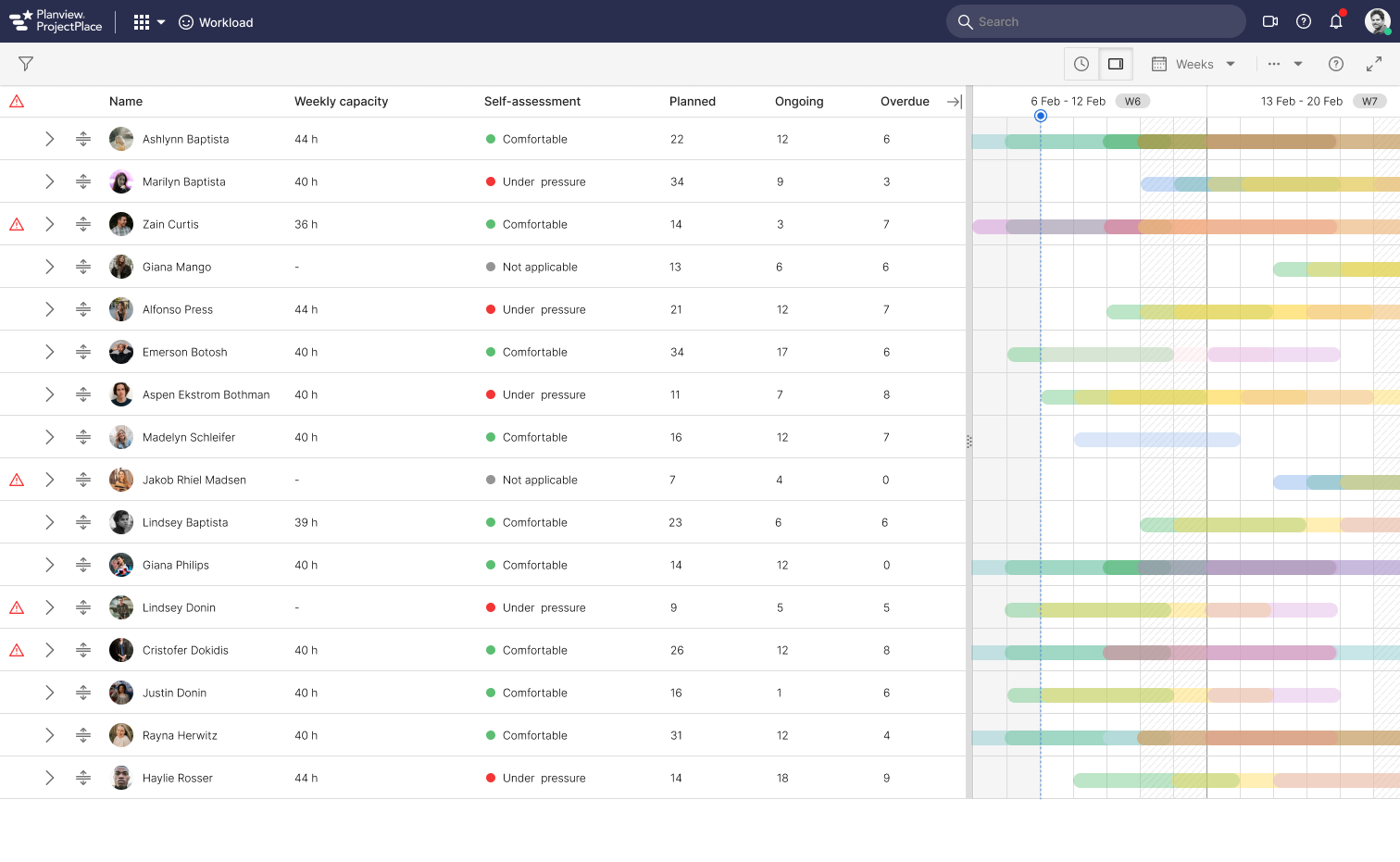
Users expressed satisfaction with the enhanced ease of assignment discovery and transfer of assignemnts. However, we recognize that software applications continually evolve based on customer feedback. While the MVP was successful, additional suggestions for improvements have been received. Some of these align with our expectations, yet were scoped due to time constraints, complexity, and shifting priorities as determined by Product managers.
Next steps
For more accurate we need to consider the following parameters while calculating user's workload.
- Calendar days (leaves).
- Reporting time when calculating workload.